Copyright © 1996, 1997, 2001, 2009 by Galen Daryl Knight
and VitaleTherapeutics, Inc.
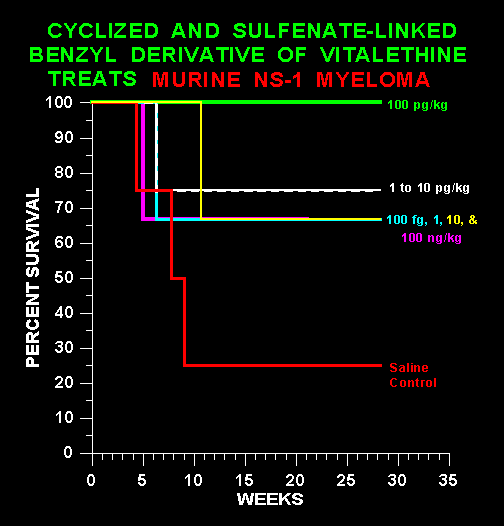
Specific Targeting, Even of Immune Tumors
Further analysis of results reported in Cancer
Research indicate that vitaletheine modulators and related
compounds
may be unique in their ability to use the immune system to selectively
treat cancers of the immune system. NS-1 myeloma is a non-secreting
plasmacytoma
of the B-cell lineage, i.e., a cancerous antibody-producing immune
tumor
which does not release its antibodies into the medium. Treatments with
the vitaletheine modulator were stopped on day 47 (almost 7 weeks) and
protracted survival after this time indicates either a cure for the
disease
in all of the juvenile mice treated with 100 pg/kg, or at least a
continuing
immune surveillance to eliminate any recurring tumor. Thus, this
approach
is sufficiently specific to stop the cancer cells without harming
rapidly
growing normal (or healthy) cells. This capacity should be particularly
useful in the treatment of young children with cancer, i.e., effective
treatment without causing the complications of retarded growth and
development
associated with other therapies, like chemotherapy and radiation.
GO TO:
